Photon Theory of Light
Photon Theory of Light: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Quanta of Energy of Radiation, Dual Nature of Electromagnetic Waves, Concept of Quantization of Energy & Rest Mass and Dynamic Mass of Photon etc.
Important Questions on Photon Theory of Light
If the energy of a photon is given as, , then, the wavelength of the photon is
Find the relation between the and using the definition of one electron volt.
Find the change in potential energy of an alpha particle in the units of , when it moves between two points with a potential difference of .
The electron volt can be used as a unit to express:
Electron volt is a unit of potential difference.
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is . What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
What is the de Broglie wavelength in associated with an electron, accelerated through a potential difference of volts?
A sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The lamp is located at the centre of a large sphere that absorbs all the sodium light which is incident on it. The wavelength of the sodium light is . At what rate are the photons from the lamp associated with the sodium light?
A sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The wavelength of the sodium light is . What is the energy per photon in associated with the sodium light? [ ]
The energy flux of sunlight reaching the surface of the earth is . The number of photons (nearly) per square meter are incident on the earth per second is (Assume that the photons in the sunlight have an average wavelength of ).
For light of wavelength , photon energy is nearly . For X-Ray of wavelength , the photon energy will be close to
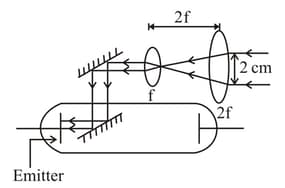
A thick parallel beam of light of frequency and power watt is directed on emitter as shown in figure. Neglect any loss of energy during reflection and refractions. If work function of emitter is then the number of photons incident on emitter plate per second is find
The energy and momentum of photon is given by and the velocity of photon will be-
A (kilo-watt) laser beam of wavelength is used to levitate a thin aluminium disk of same area as the cross-section of the beam. The laser light is reflected by the aluminium disk without any absorption. The mass of the foil is close to,
An electron-positron pair (rest mass of each particle is ) is produced by a -ray photon of energy . The K.E. imparted to each of the charged particles shall be-
Electron volt is the unit of
A hydrogen atom with a velocity absorbs a photon of wavelength and stops. If the mass of hydrogen atom is , the value of is (use )
A sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The lamp is located at the centre of a large sphere that absorbs all the sodium light which is incident on it. The wavelength of the sodium light is Then, the energy per photon associated with the sodium light is . (Approximate the answer to the nearest integer.)
A radio transmitter operates at a frequency of and a power of . The number of photons emitted per second are___
A light source is emitting radiations of wavelength . The rate of emission of photons is of the order of,
